BLOOD TESTS (Normal value and its importance)
BLOOD TESTS (Normal value and its importance) Health and Wellness
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
1.) NAME 2.) DEFINITION 3.) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) Hb or Hbg (hemoglobin)
- 2) This is the protein in your blood that holds the oxygen.
- 3) men -14 to 17 gm/dl women – 12 to 15 gm/dL
- 1) White blood cells (WBCs)
- 2) Also called leukocytes or leucocytes are the cells of the immune system
- 3) 4,500 to 10,000 cells per microliter (cells/mcL).
- 1) RBC (red blood cell count)
- 2) They carry oxygen through your body. They also help filter carbon dioxide
- 3) Men- 14 to 17 gm/dL/ women – 12 to 15 gm/dL.
- 1) Hct (hematocrit).
- 2) Is the volume % percentage of a red blood cell.
- 3) It is normally 40% for men and 31% for women.
- 1) MCV (mean corpuscular volume).
- 2) This is the average size of your red blood cells.
- 3) MCV score – 80 to 95.
- 1) Platelets.
- 2) Also called thrombocytes are a component of blood whose function is to stop bleeding by clumping and clotting blood vessel injuries.
- 3) 140,000 to 450,000 cells/mcL
- 1) ESR (Westergren) 1hr
- 2) An ESR test can help determine if you have a condition that causes inflammation. If your ESR is high, it may be related to an inflammatory condition
- 3) Male – 1-10mm/ Female – 5-15mm
Liver Function Tests (LFT)
1.) NAME 2.) DEFINITION 3.) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) Bilirubin Total
- 2) Bilirubin is a reddish yellow pigment made during the normal breakdown of red blood cells.
- 3) 0-1 mg/dl
- 1) Conjugated (D.Bilirubin)
- 2) Direct bilirubin is more soluble, less toxic, and conjugated with glucuronic acid.
- 3) 0-0.35 mg/dl
- 1) Unconjugated (I.D.Bilirubin)
- 2) Bilirubin that is bound to a certain protein (albumin) in the blood
- 3) 0.2-0.65 mg/dl
- 1) SGOT (AST)
- 2) Serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, an enzyme that is normally present in liver and heart cells.
- 3) 10-40 iu/l
- 1) SGPT (ALT)
- 2) Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase, an enzyme that is normally present in liver and heart cells
- 3) 10-40 iu/l
- 1) Alkaline Phosphatase
- 2) Alkaline phosphatase is an enzyme found throughout the body. However, it tends to be most concentrated in the liver, the bile ducts, bones, and placenta.
- 3) 40-112 u/l
- 1) Total Protein
- 2) Total Protein is a biochemical test for measuring the total amount of protein in serum. Protein in the serum is made up of albumin and globulin.
- 3) 6-8.5 gm/l
- 1) Albumin
- 2) Albumin is produced in the liver and forms a large proportion of all plasma protein. 3.5-5 gm/l Globulin group of proteins in the blood, play an important role in liver function, blood clotting, and fighting infection.
- 3) 2-3.5 gm/
- 1) Globulin
- 2) Globulin group of proteins in the blood, play an important role in liver function, blood clotting, and fighting infection.
- 3) 2-3.5 gm/l
KIDNEY FUNCTION TEST
1.) NAME 2.) DEFINITION 3.) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) Blood urea
- 2) Urea is the terminal product of protein metabolism, and 1g of protein can produce about
- 3) 0.3g of urea 10-50 mg/dl
- 1) Serum Creatinine
- 2) Creatinine is a chemical waste product in the blood that passes through the kidneys to be filtered and eliminated in urine.
- 3) 0.6–1.1 mg/dl In Women & 0.7–1.3 mg/dl In Men.
- 1) Serum Uric Acid
- 2) Uric acid is a product of the metabolic breakdown of purine nucleotide, and it is a normal component of urine.
- 3) 2.4-6.0 mg/dl (female) and 3.4-7.0 mg/dl (male).
- 1) Serum Sodium
- 2) Sodium is key to controlling the amount of fluid in your body. the body needs it for the brain and muscles to work the right way.
- 3) 135-145 mmol/L.
- 1) Serum Potassium
- 2) A potassium test is used to measure the amount of potassium in your blood. Potassium is an electrolyte that’s essential for proper muscle and nerve function.
- 3) Adults: 3.5-5.1 mEq/L or mmol/L & Children: 3.4-4.7 mEq/L or mmol/L (age dependent)
- 1) Chloride
- 2) Chloride is an electrolyte that helps keep a proper fluid and acid-base balance in the body.
- 3) 98-106 mmol/L
- 1) Total Protein
- 2) Albumin and globulin are two types of protein in your body. The total protein test measures the total amount of albumin and globulin in your body.
- 3) 6 -8.3 grams per deciliter (g/dL).
Lipid profile: Lipid profile (cholesterol and triglycerides)
1.) NAME 2.) DEFINITION 3.) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) Total Cholesterol
- 2) Total cholesterol: This is the total amount of cholesterol in your blood.
- 3) <200 mg/dL
- 1) Triglycerides
- 2) Triglycerides, another type of fat that causes hardening of the arteries
- 3) 10 to 150 mg/dL
- 1) HDL Cholesterol High-density lipoprotein
- 2) HDL, is referred to as “good” cholesterol because it helps remove LDL cholesterol from your blood.
- 3) > 40 to 60 mg/dL
- 1) LDL Cholesterol Low-density lipoprotein
- 2) LDL This is referred to as “bad” cholesterol. Too much of it raises your risk of heart attack, stroke, and atherosclerosis.
- 3) 70 to 130 mg/dL
- 1) VLDL Very Low-Density Lipoprotein
- 2) VLDL cholesterol is a type of blood fat. It’s considered one of the “bad” forms of cholesterol, along with LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
- 3) less than or equal to 2 to 30 mg/dL (0.1 to 1.7 mmol/l).
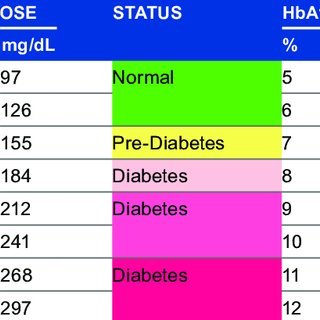
BLOOD SUGER TEST
1.) NAME- Plasma glucose test
2.) DEFINITION
3.) NORMAL RANGE
4.) Prediabetes
- 1) Random
- 2) A random blood sugar test checks your blood glucose at a random time of day.
- 3) 79–160 mg/dl
- 4) N/A
- 1) Fasting
- 2) Fasting, as the name suggests, means refraining from eating or drinking any liquids other than water for eight hours. It is used as a test for diabetes.
- 3) 90 to 110mg/dL
- 4) 110 to 125 mg/dl
- 1) 2 Hour postprandial
- 2) PostprandiaL blood glucose test measures blood glucose exactly 2 hours after eating a meal, timed from the start of the meal.
- 3) Below 140 mg/dl
- 4) 140 to 199 mg/dl
- 1) Glucose tolerance test
- 2) A glucose tolerance test measures how well your body’s cells can absorb glucose(75 gm), or sugar after you ingest a given amount of sugar.
- 3) Fasting 60 to 100 mg/dL
- 4) 1 hour <200 mg/dL | 2 hour <140 mg/dL
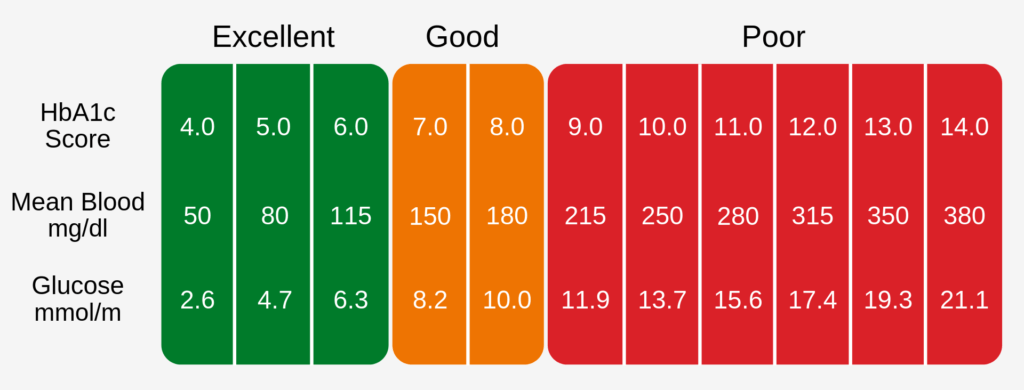
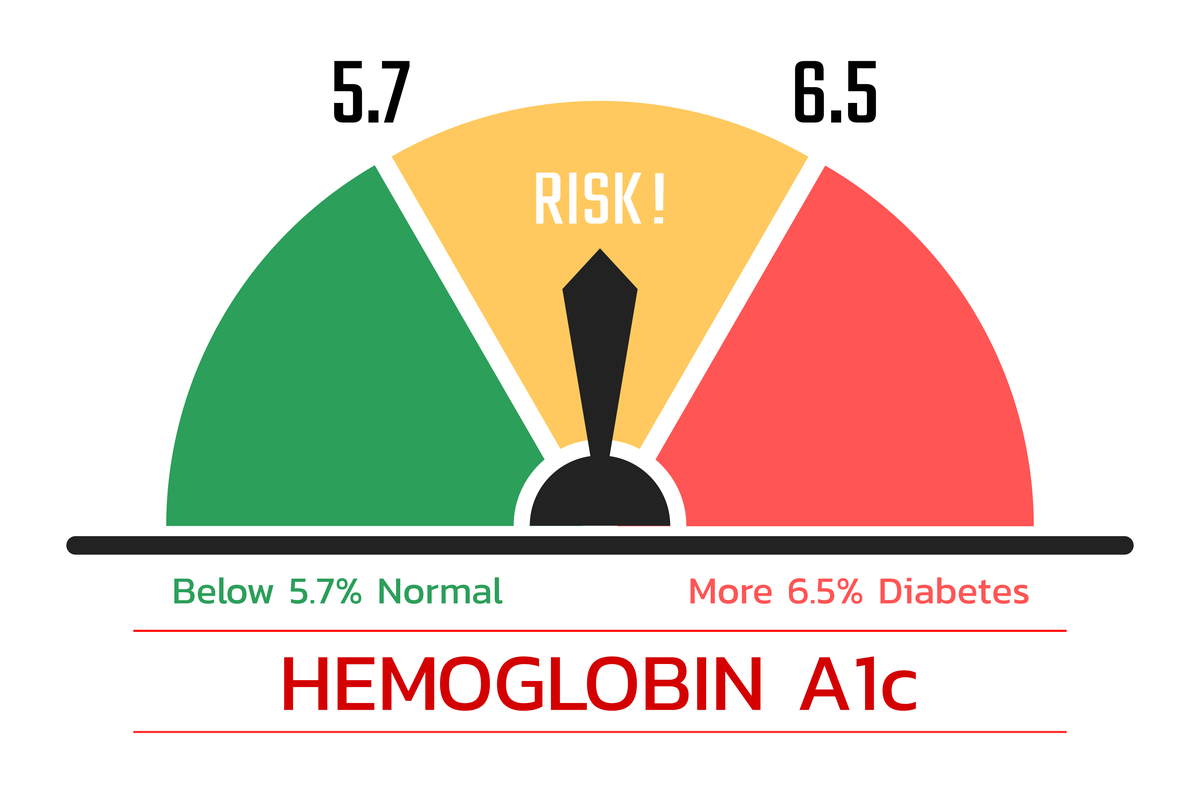
HbA1c Blood Test
HbA1c HbA1c is a marker that can determine your average blood sugar (glucose) levels over the previous 3-months
URINE TEST
1.) NAME 2.) NORMAL RANGE 3. ) DEFINITION
1) Measurement 2) Reference range
- 1) Color-
- 2) Yellow cloudy, dark, or blood-colored.
- 2) Appearance- Clear Cloudy urine may be caused by crystals, deposits, white cells, red cells, epithelial cells, or fat globules.
- 1) Specific gravity (g/ml)
- 2) 1.005-1.030
- 3) Increases in specific gravity – dehydration, diarrhea, emesis, excessive sweating, urinary tract/bladder infection, glucosuria, renal artery stenosis …
- 1) PH
- 2) 5.0-8.0
- 3) A high (alkaline) pH can be caused by severe vomiting, kidney disease, some urinary tract infections, and asthma.
- 1) Protein (mg/dl)
- 2) Negative
- 3) Protein may be present in the urine because of acute inflammation or kidney stone disease, or as a sign of kidney damage.
- 1) Glucose (mg/dl)
- 2) Negative
- 3) When blood sugar levels rise well above a target range which can occur in type 1 and type 2 diabetes-the kidneys often release some of the excess sugar from the blood into the urine.
- 1) Ketones (mg/dl)
- 2) Negative
- 3) High ketone levels in urine may indicate diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), a complication of diabetes that can lead to a coma or even death.
- 1) Bilirubin
- 2) Negative
- 3) In certain liver diseases, such as biliary obstruction or hepatitis, excess bilirubin can build up in the blood and is eliminated in urine.
- 1) Blood
- 2) Negative
- 3) Painful blood in the urine can be caused by several disorders, including infections and stones in the urinary tract. Painless blood in the urine can also be due to many causes, including cancer.
- 1) Nitrite
- 2) Negative
- 3) This test is commonly used in diagnosing urinary tract infections (UTI). A positive nitrite test indicates that the cause of the UTI is a gram-negative organism, most commonly Escherichia coli.
- 1) Urobilinogen
- 2) 0.2-1.0
- 3) Too much urobilinogen in urine can indicate liver diseases such as hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- 1) Leukocyte esterase
- 2) Negative
- 3) Leukocyte esterase is a screening test used to detect a substance that suggests there are white blood cells in the urine. This may mean you have a urinary tract infection.
- 1) WBC/HPF (WBCs per high power field, HPF).
- 2) 0-4
- 3) This test is usually ordered to determine if someone has a urinary tract infection. If both WBC and leukoesterase are elevated, it more strongly suggests a UTI.
- 1) Squamous epithelium
- 2) 0-4
- 3) The presence of squamous epithelial cells may indicate contamination of the urine specimen.
CARDIAC BLOOD TESTS
1.) Test, 2.) Definition, 3.) Normal Range
- 1) Creatine phosphokinase -MB (CPK-MB)
- 2) CPK-MB test is a cardiac marker used to assist diagnoses of acute myocardial infarction.
- 3) 5 to 25 IU/L.
- 1) Troponin
- 2) A troponin test measures the levels of troponin T or troponin I proteins in the blood. These proteins are released when the heart muscle has been
damaged, such as occurs with a heart attack. - 3) less than 0.01 ng/mL
- 1) C-Reactive Protein and Heart Disease Risk
- 2) CRP seems to predict the chance of having cardiovascular problems at least as well as cholesterol levels.
- 3) Test Result Risk- a) Less than 1.0 mg / Risk- Low
- b) 1.0-2.9 mg / Risk- Intermediate
- c) Greater than 3.0 mg / Risk High
THYROID FUNCTION TEST
1)HORMONES 2) DEFINITION 3) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) TRIIODOTHYRONINE (T3)
- 2) Abnormally high levels most commonly indicate a condition called Grave’s disease. This is an autoimmune disorder associated with hyperthyroidism.
- 3) 75 -200 ng/dL
- 1) THYROXINE (T4)
- 2) A high level of T4 indicates an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). Symptoms include anxiety, unplanned weight loss, tremors, and diarrhea.
- 3) 4.5 -11.5 ug/dL
- 1) THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH)
- 2) THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE (TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce (T4), and then (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body.
- 3) 0.3 – 5.0 U/mL
Blood Tests for Infertility
1)NAME 2) DEFINITION 3) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) FSH Follicle-stimulating hormone
- 2) It helps control a woman’s menstrual cycle and the production of eggs.
- 3) 5-20 IU/L (THIRD DAY OF MENSTRUAL PERIOD)
- 1) LH Luteinizing Hormone Level
- 2) In women, luteinizing hormone (LH) is linked to ovarian hormone production and egg maturation.
- 3) 5 – 20 mIU/ ml 25 – 40 mIU/ml (24 – 36 hours before ovulation)
- 1) Prolactin
- 2) In women, prolactin the test is done to find out why they are not menstruating, or why they are having infertility problems or abnormal nipple discharge
- 3) Non-pregnant females: 2 to 29 ng /mL. Pregnant females: 10 to 209 ng/mL.
- 1) Ovarian Reserve (AMH) Test Anti-Mullerian Hormone
- 2) The level of AMH in a woman’s blood is generally a good indicator of her ovarian reserve.
- 3) a) High (often PCOS)-Over 4.0 ng/ml
- b) Normal-1.5-4.0 ng/ml
- c) Low normal range-1.0-1.5 ng/ml
- d) Low-0.5-1.0 ng/ml
Blood Tests for Infertility
1.) NAME 2.) DEFINITION 3.) NORMAL RANGE
- 1) Vitamin B12
- 2) Vitamin B12 also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that has a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system via the synthesis of myelin (myelinogenesis), and the formation of red blood cells.
- 3) 300-900 pg/ml
- 1) Vitamin D
- 2) Vitamin D is a nutrient essential for the proper growth and formation of teeth and bones. A vitamin D test measures the level of 25- hydroxyvitamin D and/or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D in the blood to detect a deficiency or excess.
- 3) 20 nanograms/milliliter to 50 ng/mL
- 1) Serum Calcium
- 2) All cells need calcium to work. Calcium helps build strong bones and teeth. It is important for heart function and helps with muscle contraction, nerve signaling, and blood clotting
- 3) 8.5-10.2 mg/dL
- 1) Bone density test
- 2) A bone density test is the only test that can diagnose osteoporosis before a broken bone occurs. This test helps to estimate the density of your bones and your chance of breaking a bone.
- 3) A T-score -1.0 or above is normal bone density. A T-score of -2.5 or below is a diagnosis of osteoporosis.
Chikungunya
- The type of testing performed is typically dictated by the timing and volume of samples available.
- A blood test is the only reliable way to identify chikungunya since the symptoms are similar to much more deadly dengue fever.
- Common laboratory tests for chikungunya include for instance RT-PCR and serological tests.
Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis A is a liver disease caused by the hepatitis A virus.
- The virus is primarily spread when an uninfected (and unvaccinated) person ingests food or water that is contaminated with the feces of an
infected person. - The disease is closely associated with unsafe water or food, inadequate sanitation, and poor personal hygiene.
Hepatitis B HBsAg
- Hepatitis B HBsAg (also known as the Australia antigen) is the surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- It indicates a current hepatitis B infection.
Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver.
- During the initial infection, people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, abdominal pain, and yellow-tinged skin occurs.
HIV -1 & HIV-2
- HIV tests are used to detect the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome(AIDS), in serum, saliva, or urine. Such tests may detect antibodies, antigens, or RNA.
- The CD4 T-cell count is not an HIV test, but rather a procedure where the number of CD4 T-cells in the blood is determined.
- A CD4 count does not check for the presence of HIV.
- It is used to monitor immune system function in HIV-positive people.
- A normal CD4 count can range from 500 cells/mm3 to 1000 cells/mm3.
- In HIV-positive people- CD4 count below 200 cells/μL
Dengue Serology
- NS1 is a glycoprotein that is common to all dengue serotypes and can be used to detect either primary or secondary infections in the earliest stages.
- Serology testing for dengue virus-specific antibodies, types IgG and IgM, can be useful in confirming the primary or secondary diagnosis.