Unraveling the Mind Maze: Understanding Dementia and Its Impact on Cognitive Health (2023)
Dementia is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a progressive brain disorder that gradually impairs cognitive functioning, including memory loss, communication difficulties, and a decline in overall mental capacity. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of dementia, its symptoms, and its impact on cognitive health. Unraveling the Mind Maze: Understanding Dementia and Its Impact on Cognitive Health (Updated 2023 version)
Detecting the Whispers of Memory: Early Warning Signs of Dementia
Understanding Dementia
Dementia is a complex condition that involves multiple cognitive functions. It can be caused by various factors, including Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, Parkinson’s disease, and frontotemporal dementia. Regardless of the cause, the symptoms of dementia tend to be similar, including memory loss, difficulty communicating, impaired judgment, and confusion.
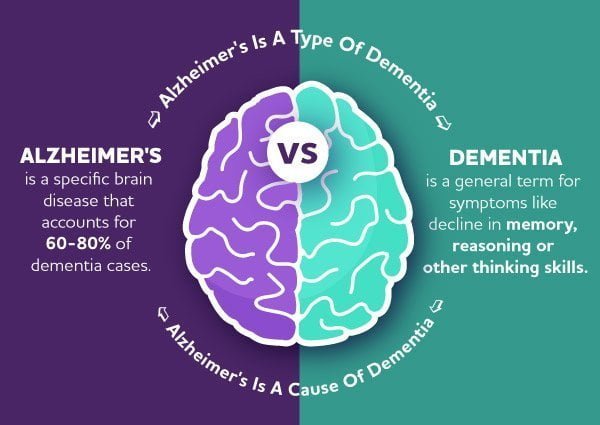
Types of Dementia
There are several types of dementia, including:
Alzheimer’s disease
This is the most common type of dementia, accounting for around 60-70% of all cases. It is characterized by the presence of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, which lead to the destruction of brain cells and cognitive decline.
Vascular dementia
This type of dementia is caused by reduced blood flow to the brain, which can lead to damage to brain cells and cognitive decline. It is often associated with a history of stroke or cardiovascular disease.
Parkinson’s disease dementia
This is a type of dementia that is associated with Parkinson’s disease. It is caused by the degeneration of dopamine-producing cells in the brain, which leads to cognitive decline.
Frontotemporal dementia
This type of dementia is caused by damage to the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, which leads to changes in behavior, personality, and language.
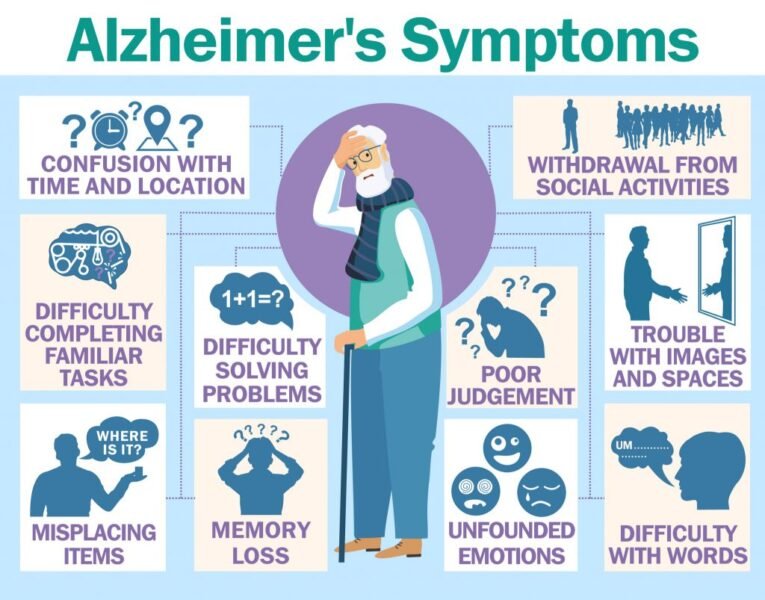
Symptoms of Dementia
The symptoms of dementia can vary from person to person and depend on the type of dementia. Some common symptoms include:
- – Memory loss
- – Difficulty communicating
- – Impaired judgment
- – Confusion
- – Changes in mood or behavior
- – Difficulty with daily activities
- – Loss of interest in hobbies or activities
Diagnosis and Treatment of Dementia
Diagnosing dementia can be a challenging process, as there is no single test that can definitively diagnose the condition. Doctors will typically perform a range of tests, including cognitive assessments, brain imaging, and blood tests, to rule out other conditions and confirm a diagnosis of dementia.
There is currently no cure for dementia, but there are several treatment options available that can help manage symptoms and slow the progression of the condition. These include medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise.

Impact of Dementia on Cognitive Health
Dementia can have a significant impact on cognitive health, affecting a range of cognitive functions, including memory, language, and judgment. As the condition progresses, these symptoms can become increasingly severe, leading to a decline in overall mental capacity.
Effects on Memory
One of the hallmark symptoms of dementia is memory loss. As the condition progresses, individuals may experience difficulty remembering recent events or retaining new information. This can have a significant impact on daily life, making it difficult to complete everyday tasks and maintain relationships.
Effects on Language
Dementia can also affect language abilities, making it difficult to communicate effectively. Individuals may struggle to find the right words or understand the meaning of words spoken by others. This can lead to social isolation and feelings of frustration and embarrassment.
Effects on Judgment and Decision Making
Dementia can impair judgment and decision-making abilities, making it difficult to make sound choices and evaluate risks effectively. This can lead to poor financial decisions, safety concerns, and other issues.
Impact on Quality of Life
The impact of dementia on cognitive health can significantly reduce the quality of life, leading to social isolation, depression,
anxiety, and a loss of independence. As the condition progresses, individuals may require assistance with daily activities, such as bathing, dressing, and eating. This can be emotionally challenging for both the person with dementia and their loved ones.
Caring for someone with dementia also places a significant burden on caregivers. They may experience high levels of stress, exhaustion, and feelings of overwhelm. It is important for caregivers to seek support and resources to ensure their own well-being while providing care for their loved ones.
Conclusion
Dementia is a complex condition that has a profound impact on cognitive health. It affects memory, language, judgment, and overall mental capacity. While there is no cure for dementia, early diagnosis and appropriate management can help slow its progression and improve the quality of life for individuals living with the condition.
Understanding dementia and its effects on cognitive health is crucial for promoting awareness, empathy, and support for those affected by this challenging condition. By educating ourselves and others, we can create a more inclusive and compassionate society for individuals with dementia and their caregivers.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
-
1. Can dementia be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent dementia, certain lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, staying mentally and socially active, and managing chronic conditions, may help reduce the risk.
-
2. What are the early signs of dementia?
Early signs of dementia may include memory loss, difficulty finding words, confusion, mood changes, and challenges with problem-solving or completing familiar tasks.
-
3. Is dementia a normal part of aging?
No, dementia is not a normal part of aging. While some memory decline can occur with age, dementia is a distinct and severe impairment of cognitive function.
-
4. Can dementia be treated with medication?
Medication can help manage certain symptoms of dementia, but there is currently no cure. Treatment plans typically involve a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
-
5. How can I support someone with dementia?
Supporting someone with dementia involves being patient, understanding, and providing a safe and supportive environment. It is essential to maintain open communication, engage in meaningful activities, and seek support from healthcare professionals and support groups.
For more information and resources on dementia and cognitive health, please visit www.optimalhealth.in
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9170-dementia
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dementia/symptoms-causes/syc-20352013
https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/what-is-dementia






